Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) has always been a major public health concern in Malaysia. What’s more alarming is the fact that the National Diabetes Registry (NDR) has recorded a surge of 20.8% for the diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus among individuals who are just above 30, affecting more than 4 million people in aggregate. The numbers are expected to keep growing exponentially considering the lack of awareness among our population.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
T2DM is a metabolic disorder that causes glucose to accumulate in the blood rather than being used as fuel in our body. When we eat, food is broken down by our digestive system into molecules that are then absorbed for the use of our body. Foods containing carbohydrates and sugars are broken down into glucose. Glucose is an important source of fuel for many organs in our body. However, to be able to use glucose as fuel, the glucose molecules in the bloodstream must first enter our body cells. The pancreas produces a hormone called insulin, a chemical messenger essential for the entry of glucose into body cells. As the blood glucose level rises after a meal, insulin is released into the bloodstream to signal the body cells to absorb glucose. In short, T2DM can be divided into two causes: the pancreas fails to produce enough insulin or the cells become resistant to insulin and ignore its messages to absorb glucose. Often, these two causes and problems are interrelated.
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
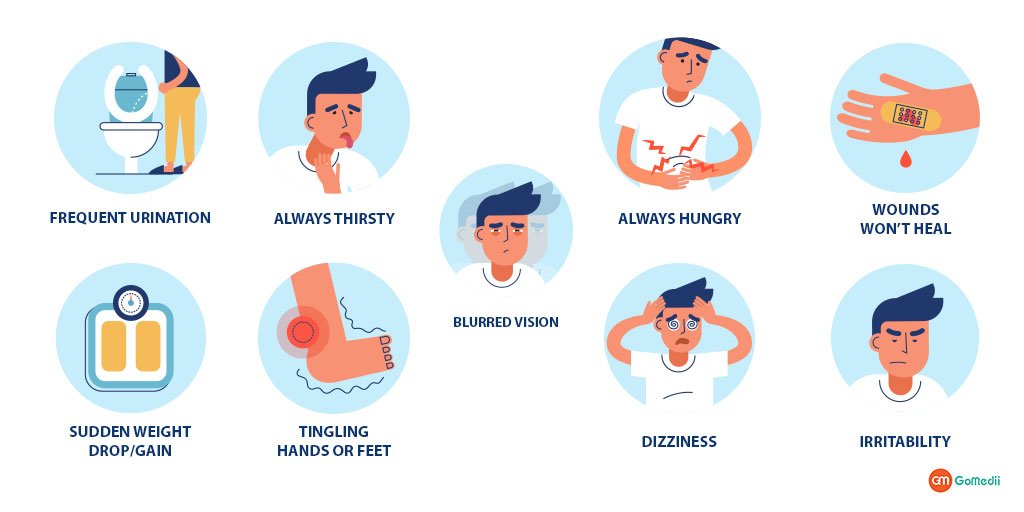
Signs and symptoms of T2DM often develop slowly, which is why many people could actually be living with this disease for years and not know they have it. The most noticeable symptoms of T2DM are frequent urination and excessive thirst. Other symptoms include:
- Increased hunger
- Unintended weight loss
- Blurred vision
- Frequent infections
- Numbness in the hands and/or feet
- Darkened skin in areas such as neck and armpit
- Fatigue
- Slow-healing wounds
These symptoms are due to chemical imbalances in the blood, related to high levels of blood glucose.
Complications of Type 2 Diabetes
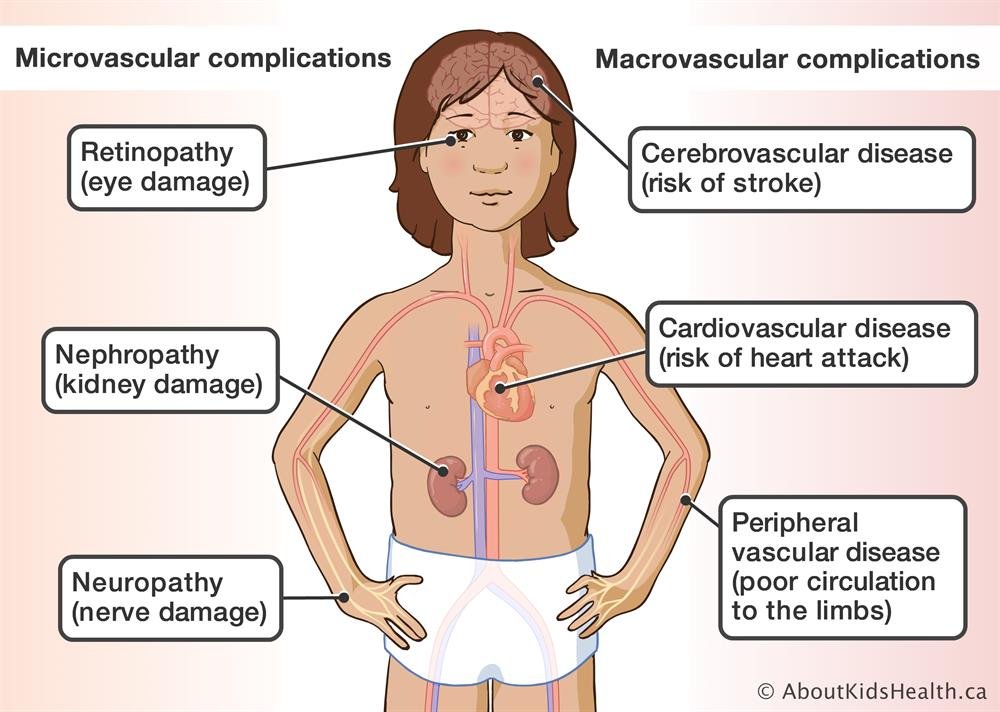
It is important to catch diabetes early. Over time, consistently high levels of blood glucose will damage the blood vessels which can, in turn, damage the organs that these vessels supply, leading to a variety of health complications.
Microvascular complications
Damage to small or micro blood vessels can cause vision problems (including loss of sight), nerve damage, and kidney disease.
Macrovascular complications
Damage to larger or macro blood vessels can lead to heart disease, stroke and poor blood circulation.
Risk factors of Type 2 Diabetes
Overweight and inactivity (sedentary lifestyle and lack of exercise) are major risk factors leading to T2DM. A positive family history of diabetes also significantly increased one’s risk of developing Diabetes. Finally, some medications may increase your Diabetes’ risk, such as:
- Thiazide diuretics
- Corticosteroids
- Drugs used to treat certain mental illnesses
- And some antiretroviral drugs used to treat HIV infections




